When you are the end user of a domain, you might decide to develop it or to redirect it to an existing website. Even if you plan to develop the domain, you can make good use of it during the development process by forwarding any traffic the domain receives to your current site. Another good example of redirecting is also used for misspellings. Google has its bases covered with common misspellings. Googel.com redirects to Google.com.
There are several types of redirects and several ways to achieve them. The most common being the 301 redirect. This isn't ground breaking news to any experienced domainers or developers, but worth a post none the less. The 301 redirect code indicates the permanent move of a page to a new address. It is also the only redirect fully understood by search engines when indexing a site. This makes it highly important when taking SEO into consideration.
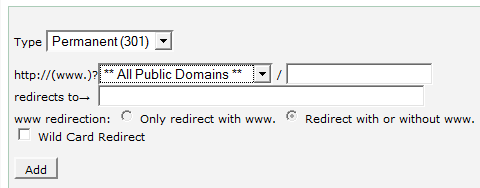
The 301 redirect can often be setup right in the cpanel of your hosting service as pictured below, if supported there. Otherwise, you can use different methods using code such as PHP or Java. You can also make the change in your htaccess file. Check out this page at WebConfs.com for further coding examples and a nice tool to check for the proper search engine friendly configuration of your redirect.
There are also pay services available that offer to redirect your domain, but those are not necessary if your server is properly configured and the options above are available to you.